

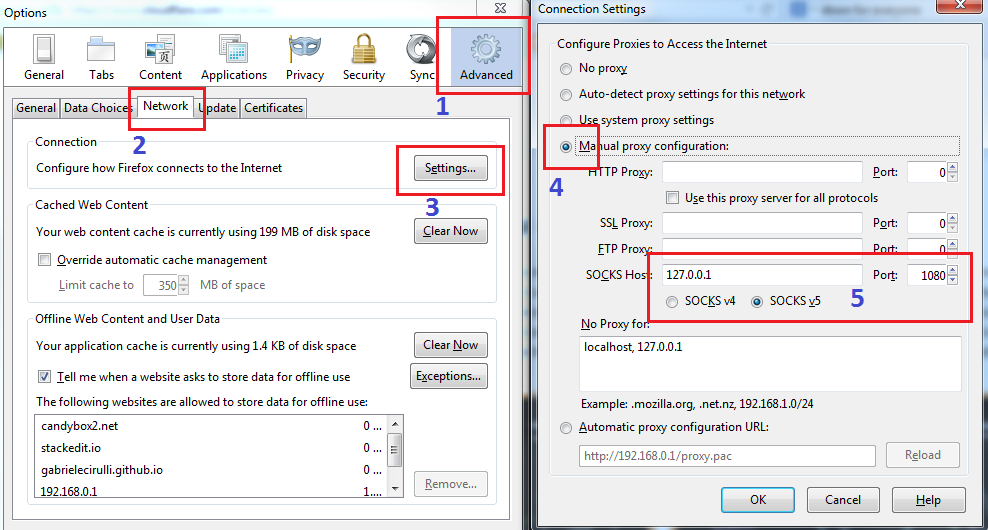
Note: Port 1080 is the IANA registered port for SOCKS, but the connection can use any other port. He can also access any other internal resources as if the browser was running on.
#Ssh tunnel manager linux manual#
In the Connection Settings window, choose Manual proxy configuration, specify localhost for SOCKS Host, 1080 as Port, and select SOCKS v5.In the General tab, scroll down at the bottom, and click on Settings.Point the browser to about:preferences.The Firefox configuration can be accomplished like this: For this to happen, the client (in our example, it is the browser) needs to be SOCKS-aware.īob can initiate an SSH session with dynamic port forwarding as follows: ~]$ ssh -D 1080 ~]$Īfter that, the browser on Bob's workstation needs to be made SOCKS-aware. In this configuration, SSH acts as a SOCKS proxy, relaying all relevant traffic through the SSH connection. To achieve this, SSH provides a feature called dynamic port forwarding, which leverages the SOCKS protocol. Connectivity and DNS name resolution should be the same as on the jump server.Having explored the previous two approaches and learned about their disadvantages, it would be great to have a third option, which brings us the best of both worlds: Prerequisites: A browser such as Firefox needs to be installed on the jump server, and an X server needs to be running on the workstation.Performance: This method usually performs rather poorly because the graphical output has to be transferred from the jump server to the workstation through the network, which is very inefficient.While this approach solves some problems of plain SSH port forwarding, it also has limitations: Only the rendering of the browser window happens on Bob's workstation. Using this method, the browser process runs on the jump server, and the connections to the web consoles of and are allowed. SSH provides a feature called X forwarding, which can be used in this situation. This situation might be a problem when using single sign-on (SSO), for instance.īob would also be to start a browser such as Firefox on the jump server and display it locally on his workstation. Redirects: When the website you are accessing redirects you to another URL, the connection fails because port forwarding is only valid for exactly this web server.TLS certificate validation: The local browser is unhappy because, in most cases, the certificate Common Name doesn't match with the hostname in the address bar (localhost), so the certificate validation fails.This approach might work well in certain cases but has its limitations: Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS security FAQīob can now point his local workstation's browser to to access the web console for, and to access the web console for.Using SSH, Bob opens a TCP tunnel for both systems, pointing to the web console port (9090) for and port 9091 for. To make sure that you don't breach any rules, please consult with your IT security representative.
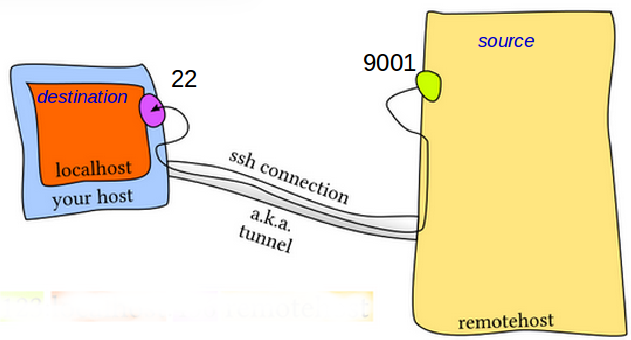
SSH command-line access to the database cluster is straightforward: ~]$ ssh ~]$ ssh ~]$ ~]$ ssh ~]$ ssh ~]$īut what if Bob wants to access the RHEL8 web console of and ? There are multiple ways to achieve this goal using SSH, all involving port forwarding of some sort.ĭisclaimer: In some organizations, security policies do not allow port forwarding. The firewall doesn't allow him to connect directly to this system from his workstation, but he can go through a jump server called. For an initial analysis, he usually uses the RHEL8 web console. Let's look at the following scenario: Bob is a system administrator at Securecorp, and he just got an alert indicating that a database cluster consisting of and is performing poorly.
It gets a bit more tricky when an administrator wants to break out of the command-line realm and use a web-based interface instead. This method usually works great as long as an administrator sticks with command-line administration. Administrators first connect to a jump server using SSH, possibly through a VPN, before connecting to the target system. Many enterprises use Secure Shell (SSH) accessible jump servers to access business-critical systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
