
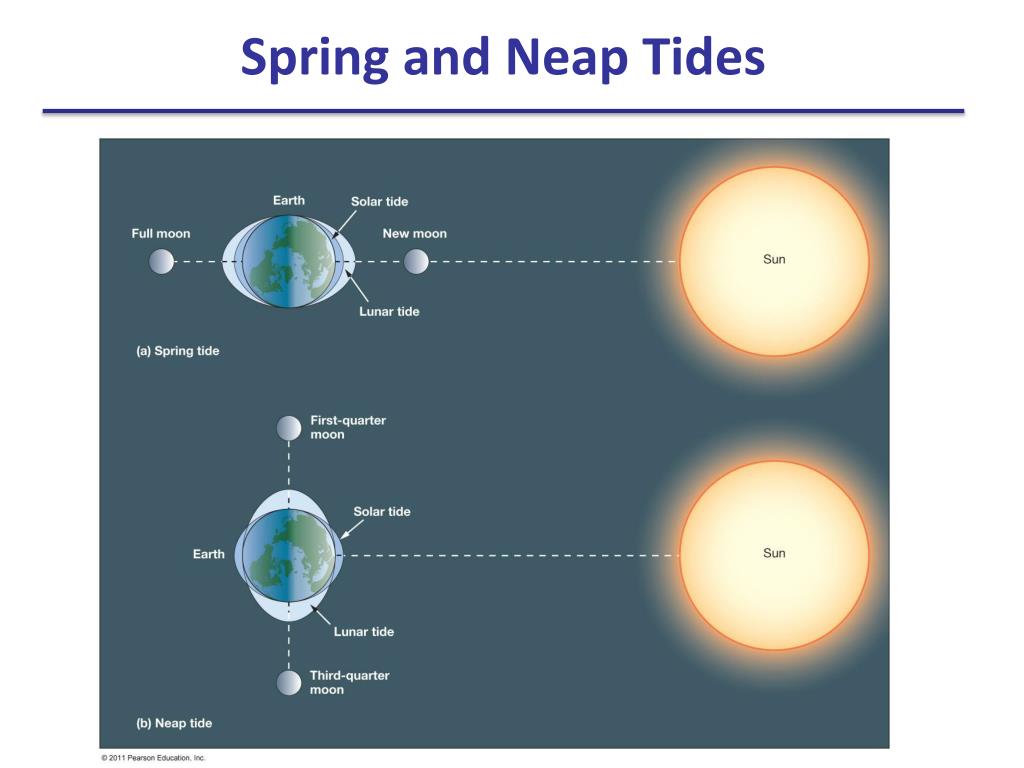
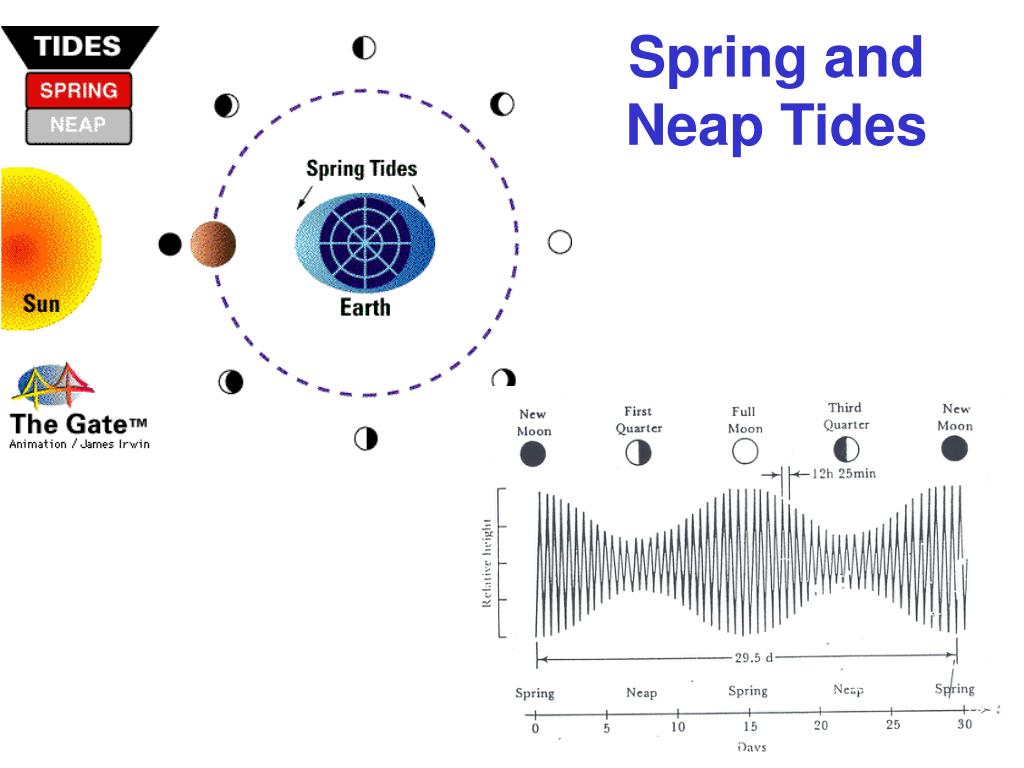
Daily tidal currents stir up water in the bay, which helps to keep sediments suspended and also re-suspended sediments that were previously deposited (Figure 5). Because most of the bay sediment is very small, mud-sized particles, it can remain suspended in the water column for many days (Figure 7). Some sediments sink to the bottom, where they collect as bay mud. Sediments are transported by streams and rivers into the delta region and then into the bay (Figure 6). Most of the sediment in the bay comes from erosion of rocks in the Sierra Nevada mountains. This lack of clarity results from an abundance of plankton and sediments that are suspended in the water. Fill out your scales with the dates on the x-axis (side-to-side) and feet on the y-axis (up and down). It also shows the phase of the Moon on each date. Whereas the visibility in clear tropical waters can be 8 meters (25 feet) or more, the visibility in San Francisco Bay is rarely more than 1 meter (3 feet). Spring Tide Neap Tide Graphing High Tides Directions: The chart below shows the height of high tide at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina over the course of a month. When most people look at San Francisco Bay, they see a dirty green color that is a strong contrast to the clear blue waters found in parts of the ocean such as the tropical Caribbean Sea. Each day these tides change 50 minutes later, as it takes the moon 24 hours and 50 minutes to completely rotate around the earth.Sediments and Bay clarity Sediments are an important component of San Francisco Bay because they transport adsorbed toxic substances, provide habitat for benthic organisms, limit light availability and photosynthesis, and are deposited in ports and waterways which require dredging. In most places on the planet, high and low tides occur twice daily. (In the Bay of Fundy, tides have a range of 44.6 ft.) In bays and estuaries, this effect is amplified. The surf grows when it approaches a beach, and the tide increases. But in shallower water, these waves collapse upon themselves as they come in contact with the sea floor. Offshore, in the deep ocean, the difference in tides is usually less than 1.6 feet. Spring tides and neap tide levels are about 20% higher or lower than average.Īnd because the tides are brought on by waves with a very long wavelength (the distance between the "crest" or tips of waves), they are affected by their interaction with the seafloor. During this phase, the gravitational pulls are canelled out, producing a smaller difference between high and low tide-also known as a neap tide. When the moon is in a quarter phase, the sun and moon are at a ninety degree angle to each other.
#Neap tide spring tide graph full
The same thing happens during a full moon, when the sun and moon line up on opposite sides of the planet-each pulling from both ends. This causes especially high high tides-called spring tides. That would mean there's even more of a gravitational pull in that direction than usual. Now suppose the sun and the moon were both on the same side of the earth, like during a new moon. Where these bulges occur, it's high tide. This forms a bulge on the side of the planet facing the moon, while the centrifugal force from the earth's rotation causes a bulge to form on the other side. (The sun only has 46% of the tide-generating force of the moon.) So when the moon faces one side of the earth, it pulls on all the earth's surfaces, but since only the ocean is flexible, only the ocean succumbs to its force. Since the moon is closer to our planet than the sun, it exerts a stronger gravitational pull on us. The tides-the daily rise and fall of the sea's edge-are caused by the gravitational forces between the earth, the moon and the sun. The TidesWhat causes the daily change in tides? Why are some high tides higher than most? And what does this all mean for the animals and plants below?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
